After 80 Million Years, Oregon's First Dinosaurs 'Discovered' Within Weeks of Each Other

In November 2018, we reported that a researcher from the University of Oregon made the first discovery of a dinosaur fossil in Oregon, a monumental find for a state that was covered by an ocean when the prehistoric creatures roamed the earth.
The fossil in question was discovered in central Oregon, near the town of Mitchell, by Greg Retallack, a researcher from the university. The find was described as "the first Oregon dinosaur fossil ever reported in a peer-reviewed scientific journal' in a post on the university's website.
Those last five words are an important caveat, though, says Dave Taylor, previously a researcher at U of O and now president of the Northwest Museum of Natural History.
After the November story was posted, Taylor emailed the Oregonian/OregonLive to point out that a fossil was discovered at Oregon's Cape Sebastian in the mid-1960s, excavated in the 1990s and was, just recently, confirmed to be that of a duck-billed dinosaur.
A discovery in fits and starts
In the early 1960s, Taylor said, a crew from the U.S. Geological Survey happened upon the fossil at Cape Sebastian, an outcropping of sandstone near Gold Beach on Oregon's southern coast.
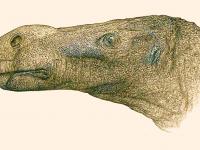
In 1969, a pair of professors from the University of California, Berkeley, traveled north to inspect the fossil and confirmed that it was the sacrum, or fused vertebrae, of a duck-billed hadrosaur.
And then the fossil sat in the rock for nearly 30 years, much as it had for the previous 80 million or so, before Taylor and a team went back to the cape in 1994 to excavate the ancient bone.
"The fossil appeared in grainy, brownish-gray relief, like a rock inlay, in the otherwise light gray slab of sandstone at the tip of the cape," The Oregonian reported in 1994. "At low tide on a calm day, it was 15 feet above the crests of the gently rolling swells. Just above it, the forested nose of the cape rose sharply toward U.S. 101."
More than 2 feet long and roughly 70 pounds, getting the fossil out of the rock proved no easy task. With the help of a cadre of volunteers, many of them children from around Oregon, Taylor pulled the fossil from the rock and showed it to a number of experts, all of whom agreed that the bone came from a hadrosaur.

And then he brought it up to Portland where, again, it would sit for a three-decade spell before he could turn his attention to it.
It wasn't until he retired in 2013 that Taylor finally had time to prepare the fossil, carefully chipping away at the sandstone that still clung to it, for description in a peer-reviewed paper.
A second 'first'
In 2015, while Taylor was working to prepare the Cape Sebastian fossil, University of Oregon earth sciences Professor Greg Retallack was in central Oregon, leading a field expedition of students looking for fossilized plants near the town of Mitchell at a hotspot for ancient rocks called the Hudspeth Formation.
The group came upon a pile of ammonites, spiral shaped sea creatures that went extinct around the same time as the dinosaurs. Sitting there, on top of the pile, was a bone, Retallack recounted.
"I knew immediately what it was," he said. "The students were a bit mystified, but I was thrilled."

The fossil, a toe bone, belonged to a creature called an ornithopod, a 17-foot-long herbivore that weighed up to 1,500 pounds and walked on two legs. The fossil is thought to be roughly 103 million years old, dating back to the Cretaceous period.
Back then, the Pacific Ocean stretched far inland from the beaches we know today, and the coast started at the Blue Mountains in what is now eastern Oregon. The shoreline was rocky and rugged, and everything west of present day Wallowa was under water.

Source: www.oregonlive.com